I gave a talk at AAG last week, as part of a session about OpenStreetMap data analysis. [UPDATE: I gave a similar talk at State of the Map US in Seattle on July 23, 2016. You can watch the video on YouTube. UPDATE #2: Maurizio Napolitano translated this post into Italian!]

I followed three presentations by some of my favorite OSM researchers, Sterling Quinn (@SterlingGIS), Indy Hurt (@IndyMapper), and Jennings Anderson (@JenningsatCU), all of them using OSM history data to see what it tells us about OSM’s past and its present. You can read more about their presentations in Diana Stinton’s article for Directions Magazine: “The simple map that became a global movement.”
My own dissertation research also looks at OSM’s history data, but for this presentation I wanted to try speculating about OpenStreetMap’s future. Specifically, what if you take a chart that looks like this, and extrapolate what happens if the number of nodes keeps going up up up:
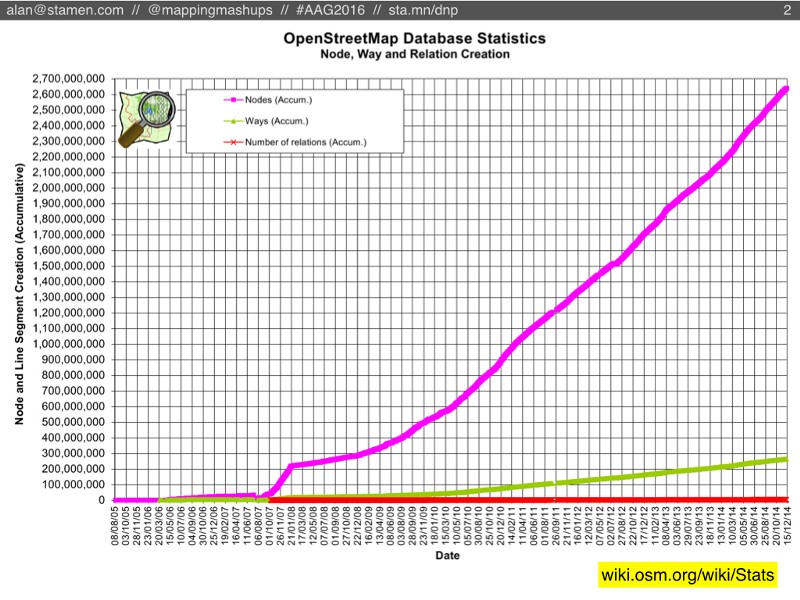
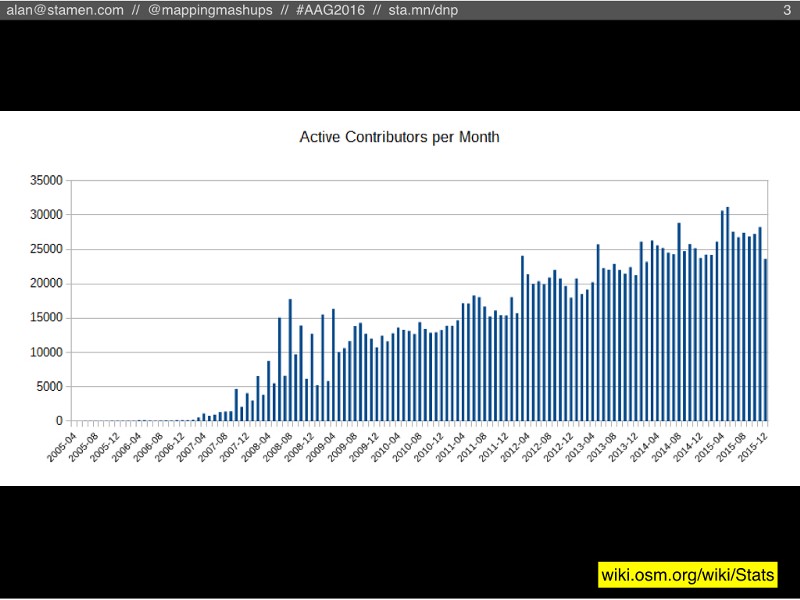
Like all of my co-presenters, we’re really not that interested in counting nodes, but we’re more interested in what those nodes tell us about the people who make up OpenStreetMap. You may have heard recently that OSM passed 2 million registered users, but the reality is that most of those people have never even edited OSM. A more meaningful statistic is the count of users who have been active editors each month. Right now the number is around 25,000 people. Smaller than 2 million, but still steadily increasing:
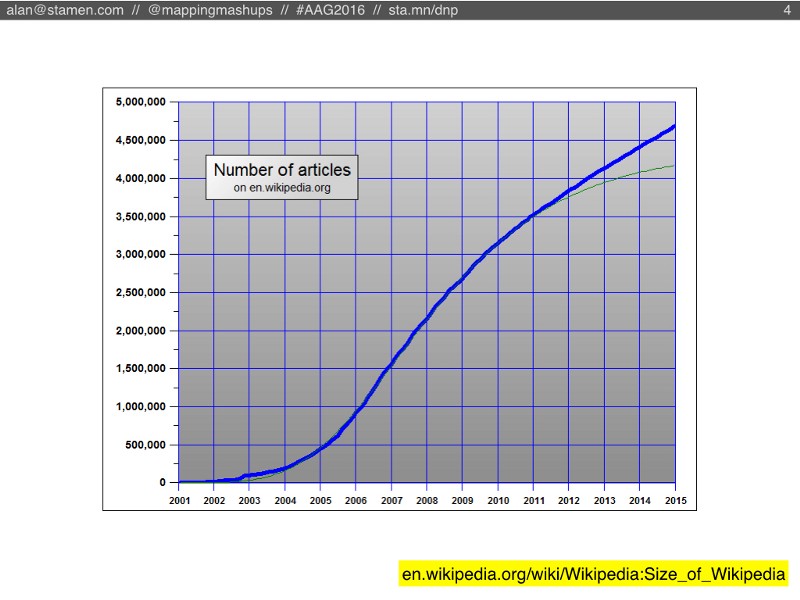
In my research I make a lot of comparisons with Wikipedia, which is a much bigger and older project than OSM, but similar in many ways. Wikipedia is also still growing in size, but if you look closely you’ll see that the rate of new articles has been slowing down for a long time, since 2007 approximately.
The same thing is true about Wikipedia’s users. Their monthly count of active editors has been dropping since 2007. A smaller number of people is doing more and more of the work.
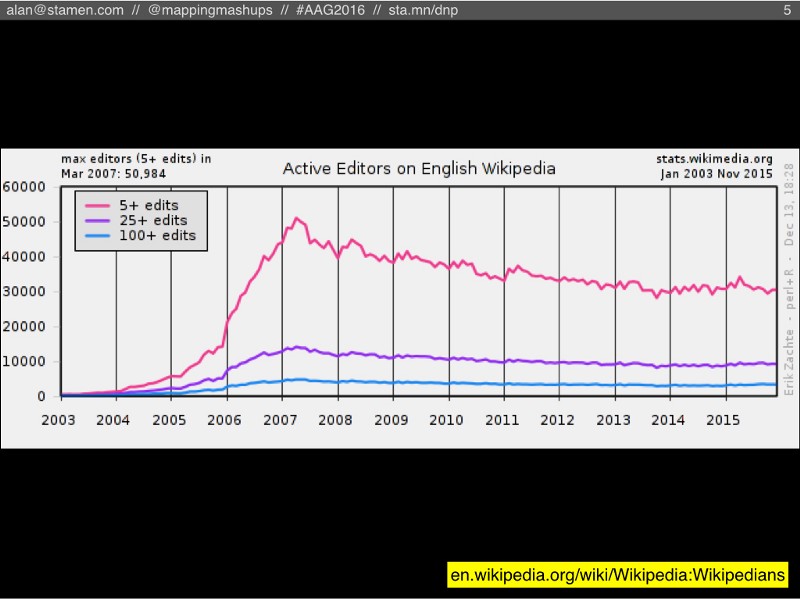
If you talk to Wikipedia researchers, they’ve been freaking out about this statistic for a long time. Nobody knows exactly why it’s happening. It’s probably caused by a variety of factors, and one possibility (to simplify things greatly) is that the Wikipedia community has become increasingly unwelcoming and difficult to become a part of. Or at least that there are enough difficult people to deal with that it drives away new contributors. (Those who have been active in the OSM community might notice some parallels here.)
Another possible reason is Wikipedia’s Notability Guideline. Basically, Wikipedia has come to a consensus that there are only some topics that are notable enough to be in an encyclopedia. Any new articles that aren’t considered notable are candidates for speedy deletion.
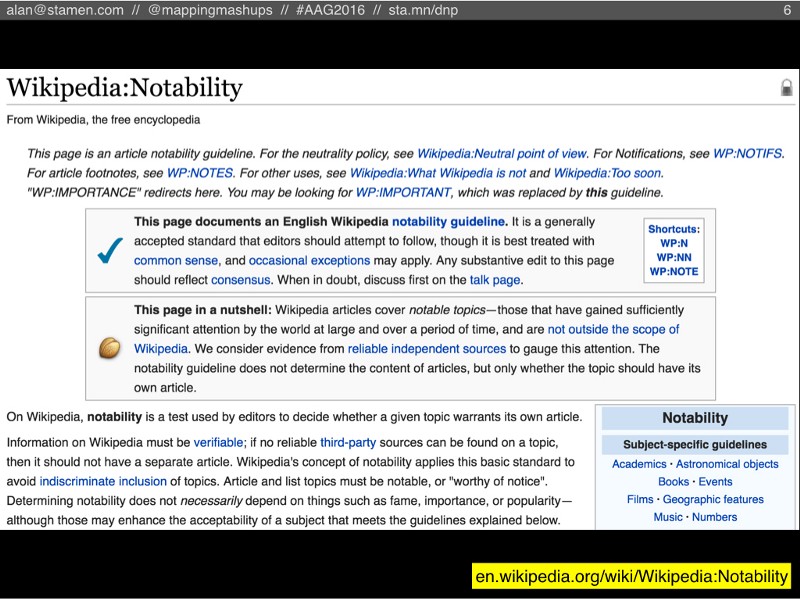
Of course, there are many Wikipedians who argue that Wikipedia shouldn’t be held to the standards of a traditional encyclopedia: there are no space constraints because it’s not printed on paper, so why not have an article about basically everything, notable or not?
These two factions became known as Inclusionists and Deletionists, and pretty much everyone agrees that the Deletionists won.
However, this is one of the key places where OSM differs from Wikipedia. OpenStreetMap has no notability rule! An arbitrary amount of detail is theoretically possible. When you’re done mapping roads, you can start mapping sidewalks. When you’re done with sidewalks, you can map mailboxes, trees, and benches. Nobody knows where the level of detail will end.

But if OSM allows this much detail, somebody has to maintain it!

This question of maintenance is the key focus of my dissertation research. Who maintains OSM? Are they the same people who mapped the roads to begin with, or do different people come along to do maintenance? Is there enough maintenance happening to keep OSM up-to-date?
In my research I call this “map gardening”, borrowing the concept of “wiki gardening” from the community of wikis (Wikipedia being only one of these). A wiki gardener is someone who doesn’t necessarily write new articles, but instead enjoys fixing typos and grammar in existing articles, fixing up formatting and broken links, basically doing all the thankless and unsexy tasks that are necessary to keep a wiki functioning. Presumably a similar “map gardening” must exist in OSM, so what does it look like?
And what does it look like going into the future?
Here I’d like to step back, way back, and borrow an analogy from cosmology, the study of the life and death of the universe. Following the Big Bang, the universe expanded rapidly. After a while, the expansion slowed down, but recent studies have found that it’s actually speeding back up again. Cosmologists think there is something called dark energy that is causing this acceleration, but nobody knows how much dark energy is out there. If it’s a lot, then the universe will keep expanding and eventually even molecules and atoms will be torn apart. This is called the Big Rip. If there’s not much dark energy out there, then eventually gravity will overcome it and the universe will collapse into the Big Crunch.
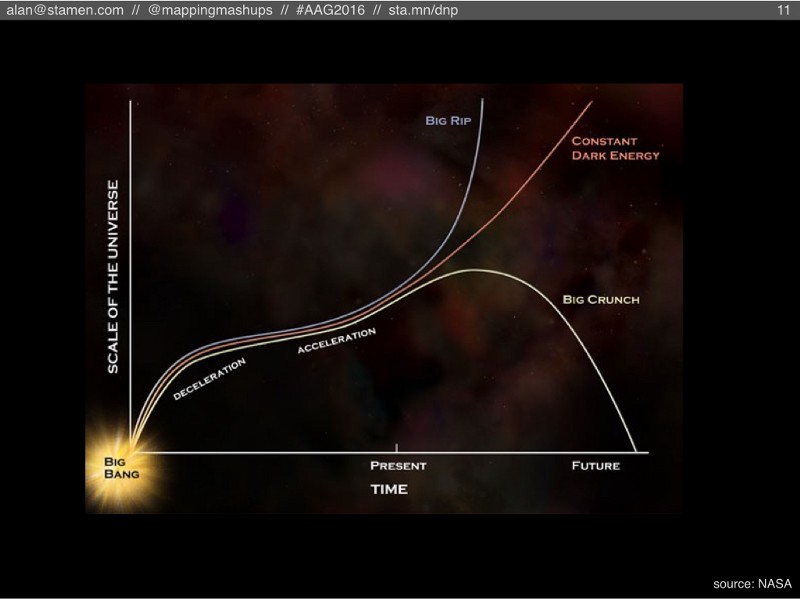
So what are the “cosmological” futures for OSM? The number of new features (points, lines, polygons) could keep increasing, or maybe that pace will slow down or stop entirely. Similarly, the amount of maintenance edits (those “map gardening” tasks) could keep growing, or they could slow down to a trickle. The balance between those two activities could lead to the OSM equivalent of a Big Rip, a Big Crunch, or something else entirely.
Here are (at least) four scenarios that might occur:
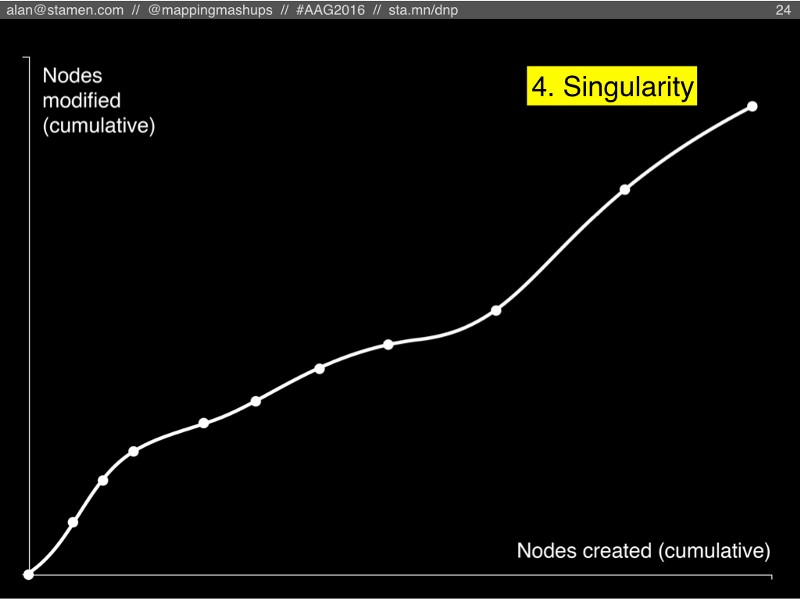
But before we look at those scenarios, here’s a chart (not with real data, yet) that illustrates the possibilities. Note that this chart is different from the cosmological chart that I just showed. Instead of time along the bottom axis, this is a cumulative chart where time moves somewhere up and to the right.
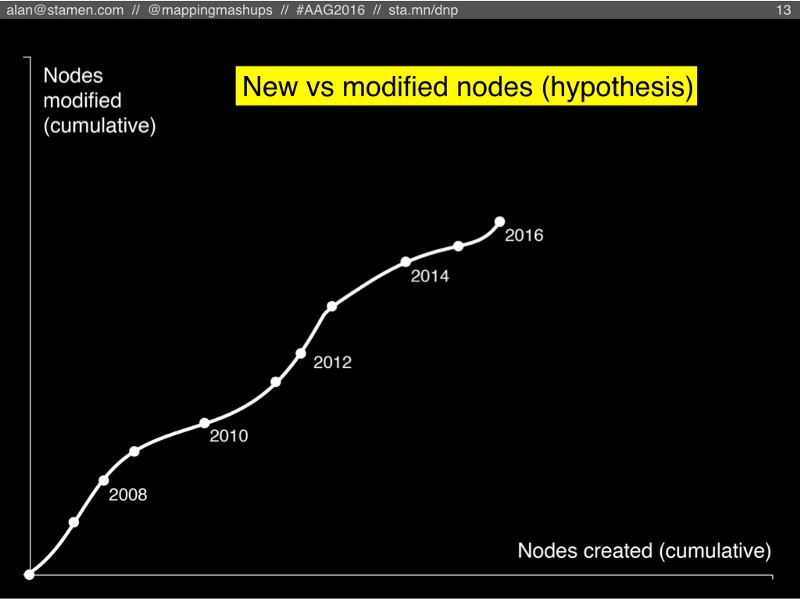
As people create new nodes in OSM, the dot moves to the right. Every time someone edits an existing node, the dot moves upward on the chart. Because it’s cumulative, the line will never curve downward, or bend backward to the left. Each year’s worth of edits moves the dot some amount right, up, or both. (Also note, for simplicity’s sake I’m ignoring all the lines and areas in OSM, and only looking at the raw points, which OSM calls “nodes”).
Now let’s look at the four scenarios.
#1. Ghost town
Our first scenario is the “Ghost town”, where new nodes slow down, and so do the modifications. Basically, this is what happens if everyone gets bored of OSM (or if community disfunction causes everyone to leave).
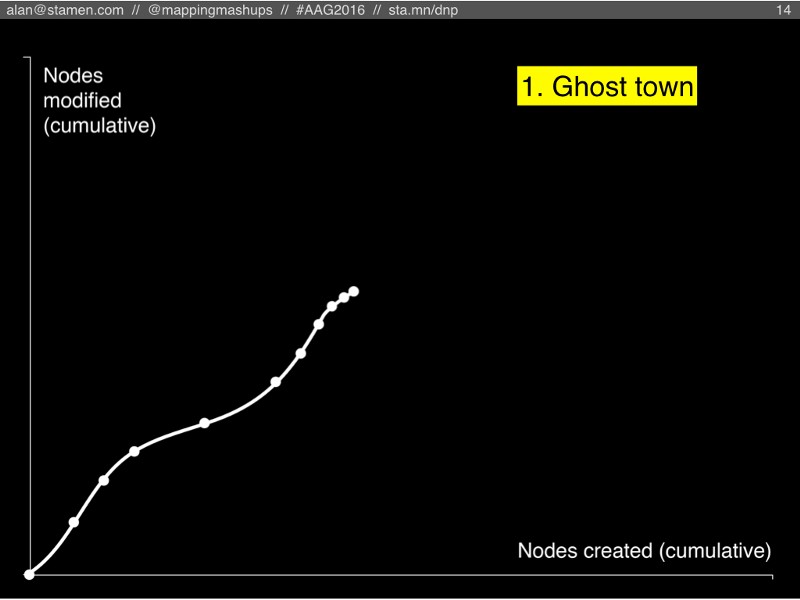
It wouldn’t necessarily look like this: (although this is the first result when you search for “ghost town” in OpenStreetMap).
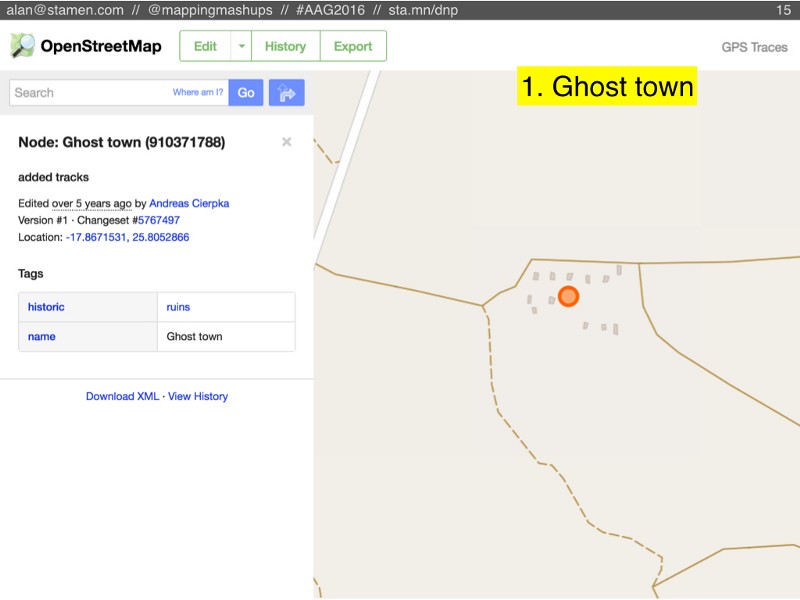
In fact, the Ghost Town scenario might look like a fully complete street map. But it would be slowly getting out of date, and no one would be increasing the amount of detail. It would become a snapshot in time.
#2: Garden
The second scenario is what happens if people stop adding new features to OSM, but they continue to edit them and keep them up to date. Maybe this would happen if OSM institutes something like Wikipedia’s Notability Rule. Perhaps OSM decides that streets and addresses are good to have, but trees and mailboxes are too much detail.
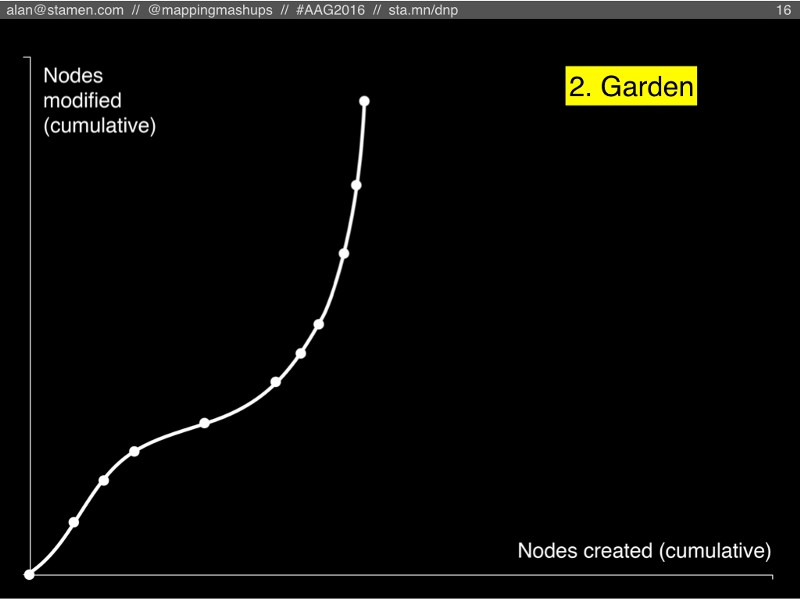
But this scenario requires a large community of OSM editors who enjoy maintenance. There will always be new buildings built and old ones torn down, roads that are widened or redirected, river banks that change their course. All of these things need to be updated in OSM if it’s going to stay useful.
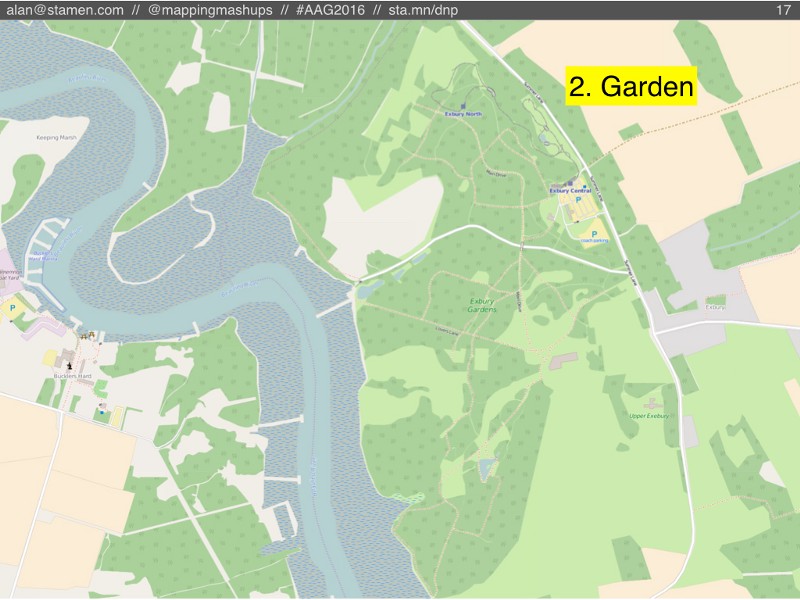
For example, here’s a nice garden in OSM, next to some well-mapped riverbanks that will be shifting and changing year after year.
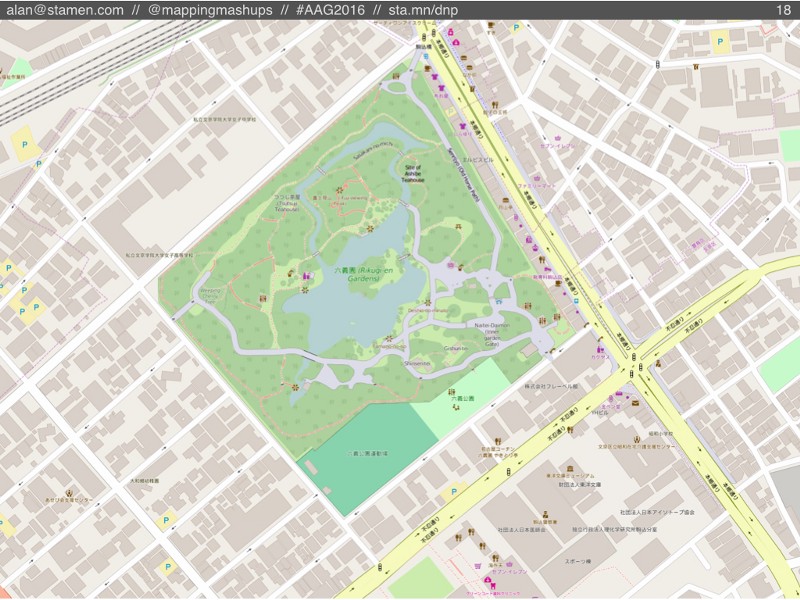
Here’s another lovely garden. (Of course, I’m talking about all kinds of OSM features, not just literal gardens… but if you do find any nice examples of gardens in OSM, please send me a tweet!)
#3: Borgesian map
The third scenario is what happens if people keep adding more and more detail to OSM, but nobody can keep up maintaining it.
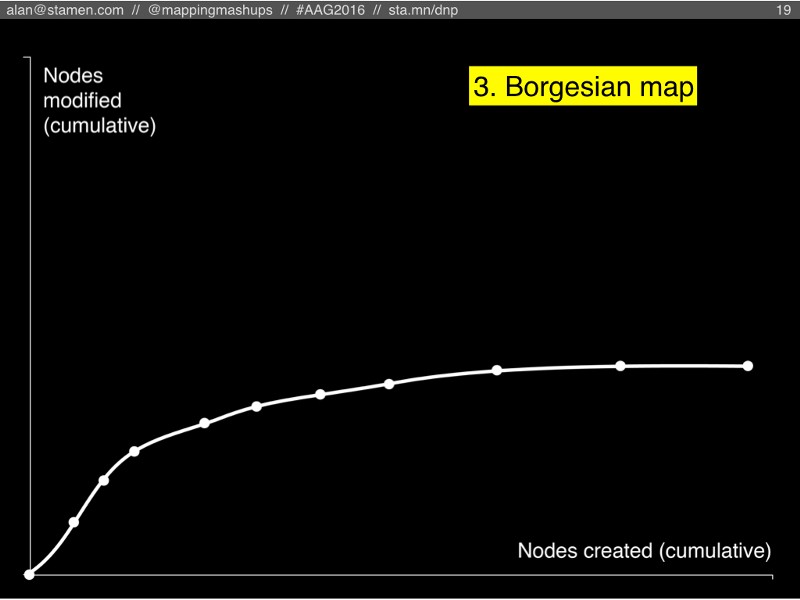
In this scenario, eventually everyone has mapped all the streets and sidewalks, and they start mapping every tree and shrub, maybe even every blade of grass (to borrow Harry Wood’s “most insane” example from his 2011 talk at State of the Map about OSM as a garden).
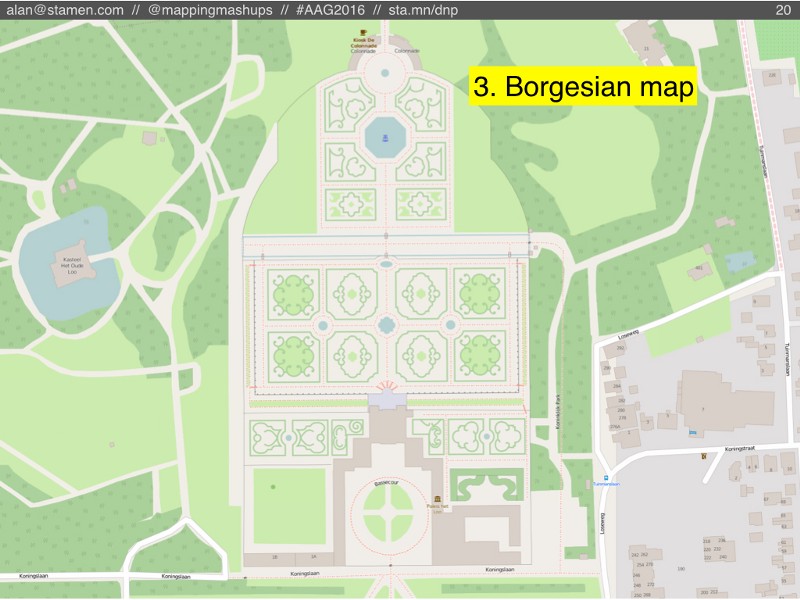
Eventually, OSM would approach the 1:1 scale map described by Lewis Carroll, and later in a short story by Jorge Luis Borges. In Borges’s story, cartographers succeeded in creating a 1:1 map, only to find it impossible to use. Eventually they abandon the map, parts of which can still be found scattered about in the desert.

In OSM, a 1:1 map without enough maintenance would be equally useless. It might not be fully abandoned, as people keep adding more and more data, but everything they did add would become out-of-date and impossible to verify. The OSM database would be cluttered with useless information.
But we’re probably not yet at the limit of detail that is both useful and (potentially) maintainable. OSM already has some proposals underway about mapping roads as areas instead of lines. Here’s an example of some municipal data (not from OSM) visualized by Lou Huang at Mapzen, showing curblines maintained by the city of Philadelphia. I won’t be surprised is OSM volunteers start adding data at this resolution.
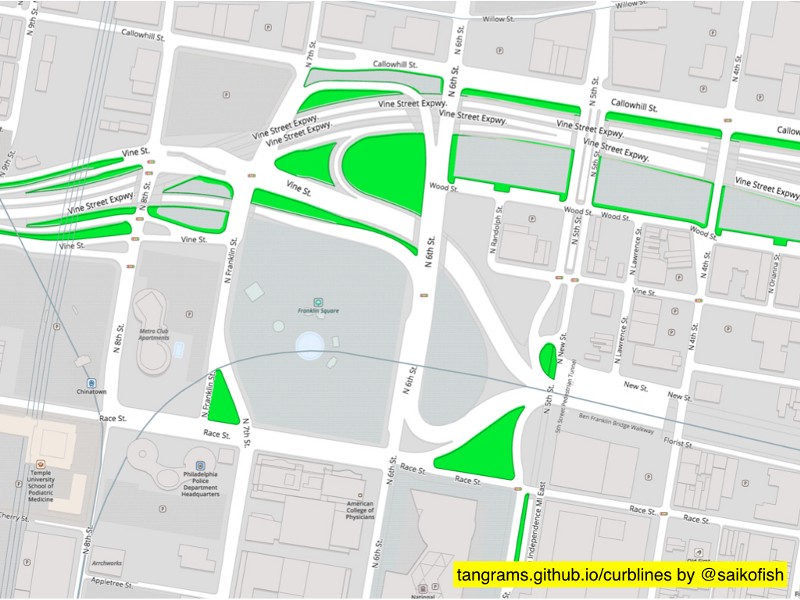
But then where do we stop? As another example of municipal micromapping, here are the outlines of all the street markings painted by the city of Cambridge, Massachusetts. Surely some amateur mapper in Germany with too much time on his/her hands is thinking about how to tag features like these in OSM…
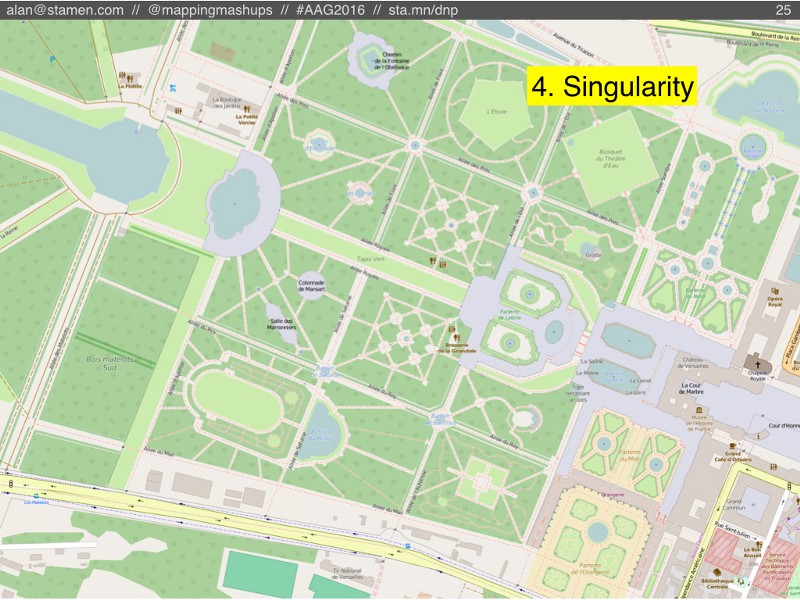
#4: Singularity:
But what if Borges’s 1:1 map doesn’t get abandoned to crumble apart in the desert? What if, somehow, OSM keeps adding features, but the community keeps maintaining those features too? What if OSM didn’t just have 25,000 monthly editors, but actually did have 2 million or 25 million editors checking OSM and fixing data every day?
I’m calling this scenario The Singularity, but you’ll have to excuse me for mixing my metaphors. I’m not talking about a cosmological singularity like a black hole, or the Big Bang. Instead I’m borrowing from Ray Kurzweil’s idea of rapidly accelerating computational power and information growth. Partly I like this concept because the singularity is the point past which we can’t predict or imagine what would happen, and I can’t really imagine what OSM would look like if it were a constantly-maintained 1:1 map. But Kurzweil’s singularity is also relevant because OSM probably couldn’t achieve a perfectly up-to-date 1:1 map without the help of algorithms and machine intelligence. But that’s a topic for another presentation.
Who knows what that would look like? The gardens of Versailles in OpenStreetMap are the most detailed gardens I could find, but this level of detail might only be the beginning.
Reality
So we’ve spent a lot of time speculating about what these different scenarios might look like, and I’ve shown charts that illustrate how we might see those scenarios manifest themselves in the data. But what does the real data look like?
Here’s the chart showing the OpenStreetMap planet file, from the earliest OSM nodes around 2005, up to January 1st 2016. The line shows the cumulative count of nodes created and nodes edited for each month, with dots every January.
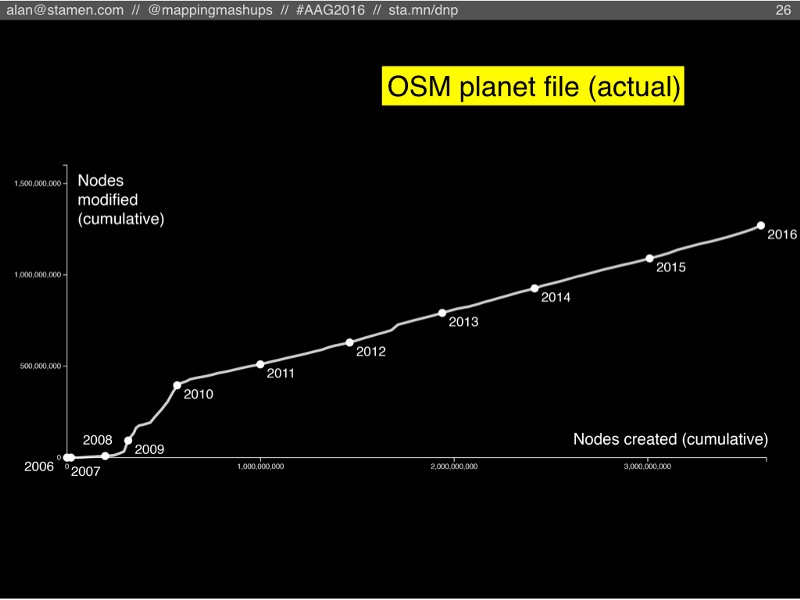
There are a few surprising things about this chart that I didn’t expect to see. In the first few years, we see mostly new nodes added, and not a whole lot of modified nodes; that’s to be expected. You can see there were more new nodes in 2007 than there were in 2008, mostly due to the TIGER data import that happened in late 2007. Then in 2008 and especially 2009, we see a significant number of modifications. I’m not sure what was happening during this time to explain this burst of gardening. It doesn’t correlate exactly with changes in the OSM data structure (which might require fixing features that were incorrectly translated from one datatype to another), and it doesn’t match up with the availability of new higher-resolution satellite imagery (which might have triggered spurts of gardening where people would improve the geometry of poorly-traced roads). That early spike of gardening certainly merits more research.
The other striking aspect of this chart is the steady, smooth line from 2010 to the present day. It’s shocking to think that when you sum up all the editing activity all over the world in OSM, it always adds up to the exact same ratio of new features to modified features. From 2010 onward, every month in OSM, there were roughly three new features for every one modification of a feature. Did OSM stumble upon some perfect, magic balance that will be maintained forever? What is special about that ratio?
But if the study of geography teaches us anything, it’s that you can’t look at the whole world as a homogenous system. We need to zoom in on the local dynamics of the OSM community, not just look at the planet file as a whole. How has OSM evolved on smaller scales?
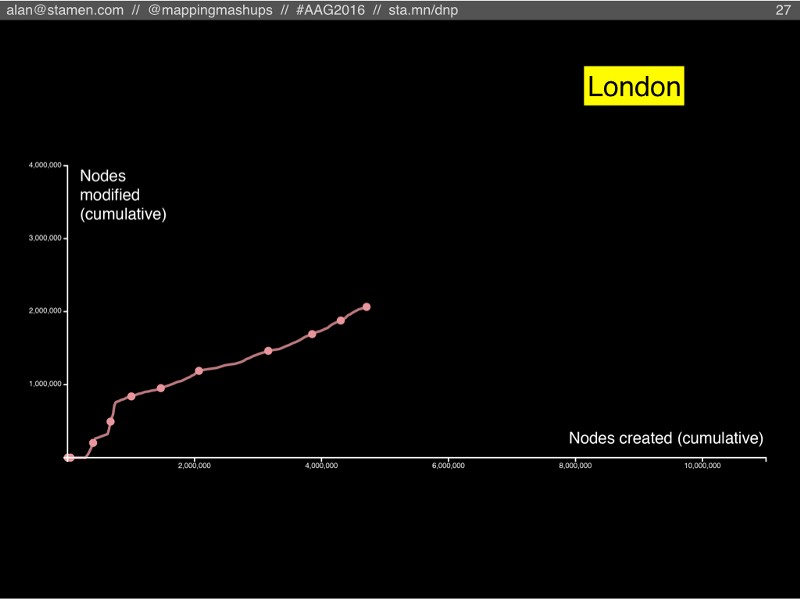
Here’s London, the place where OSM got started. It follows a similar path as the planet does overall. But if you look closely the spacing between years, it starting to slow down (even while the ratio between node creation and node modification is staying steady). Is London pulling back from a course towards the singularity? If it slows down too much, will it become a ghost town? Maybe the map of London is getting close to being “finished”?
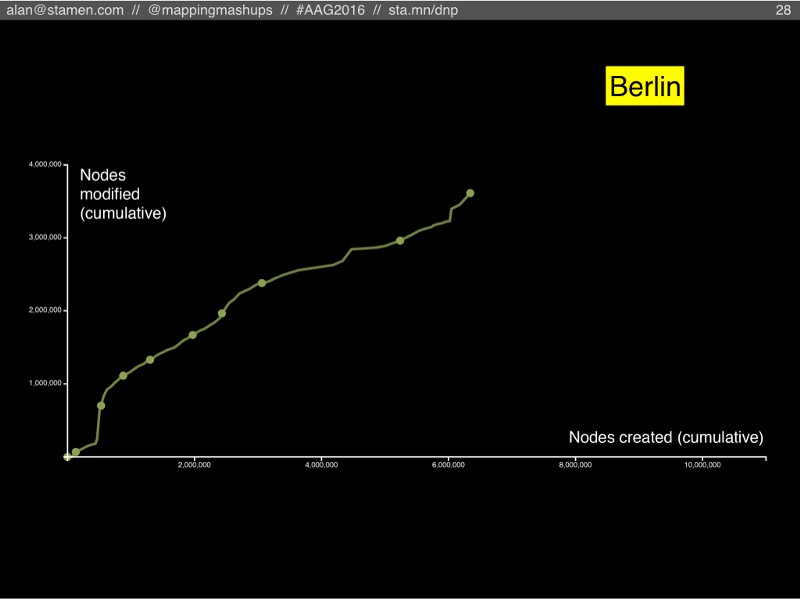
However, if we look at Berlin, another extremely well-mapped city with a strong OSM community, we see something different. In the last two years, when London slowed down, Berlin sped up! Here they are still finding new things to map.
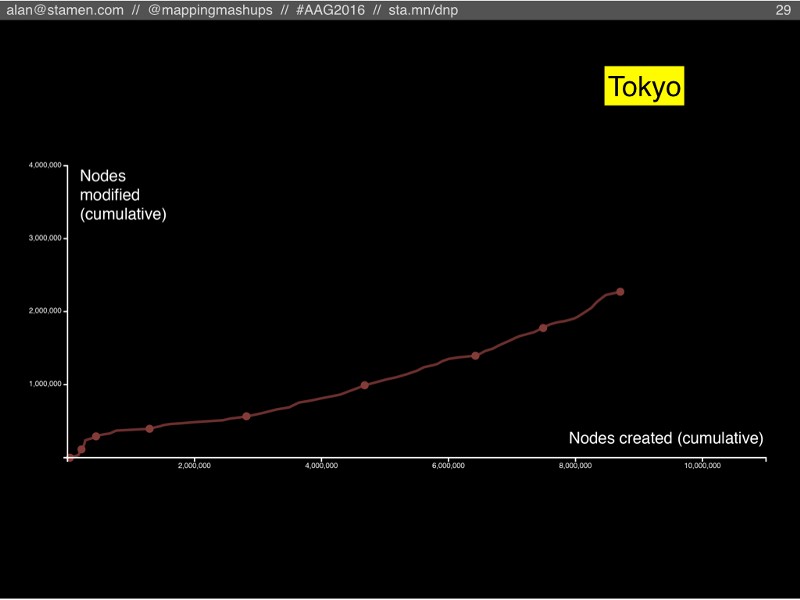
Tokyo is also still adding new features, although it might be slowing down a bit, like London. But one key difference between Tokyo and the first two is that the number of modified nodes is significantly lower compared to created nodes (the chart is further down toward the right). Tokyo is more on track to become a Borgesian map.
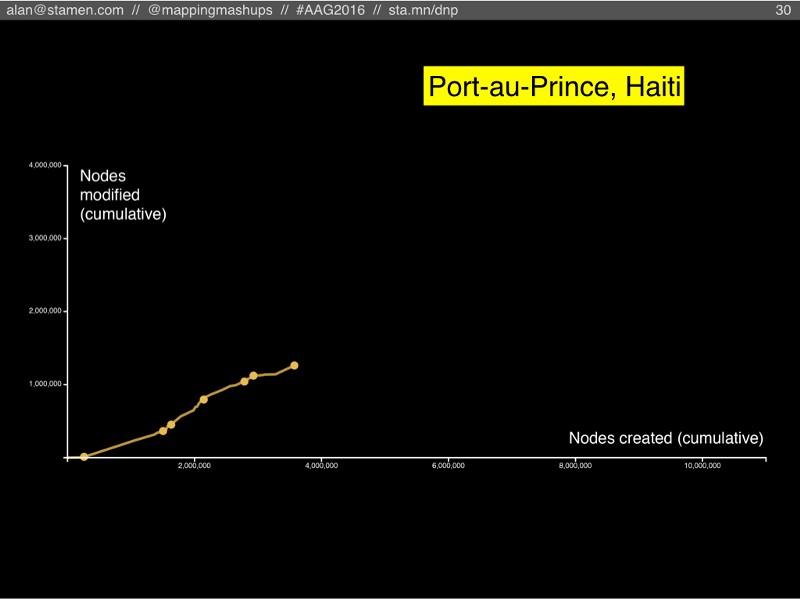
In a place like Port-au-Prince, Haiti, we can see the signature of an intense burst of humanitarian mapping after the 2010 earthquake. We also see sporadic bursts of subsequent activity: in some years there is almost no activity, but in other years there is a lively pace of new features with a bit of maintenance. This is an example of a place where a community is struggling to take root and avoid becoming a ghost town.
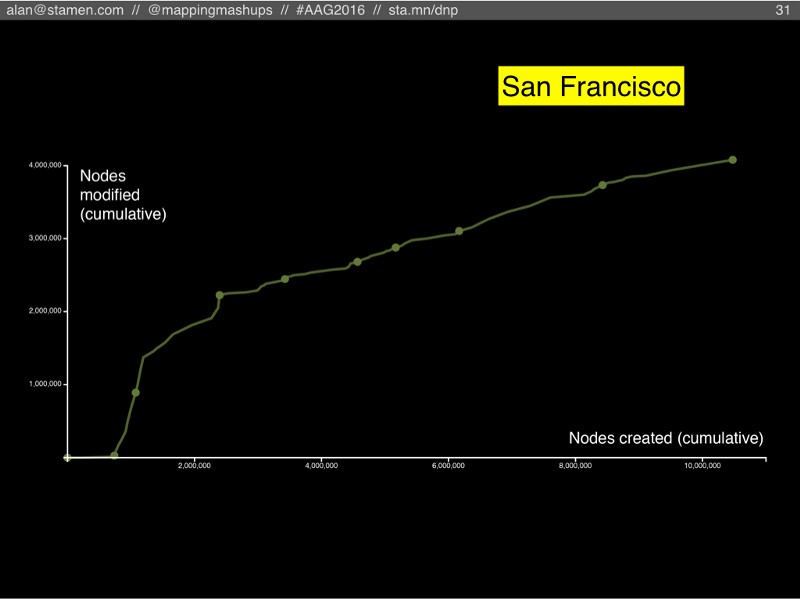
In San Francisco we can see the early influence of the TIGER import (the first year which is flat against the X axis: all new imported nodes, no maintenance). But in later years we see a strong and growing rate of activity: in relative terms, the TIGER data is just a blip, far in the past. More worrisome is the trend of the line, bending more towards the right instead of upwards. If San Francisco doesn’t increase the amount of gardening edits, all this rich data will become out of date and obsolete.
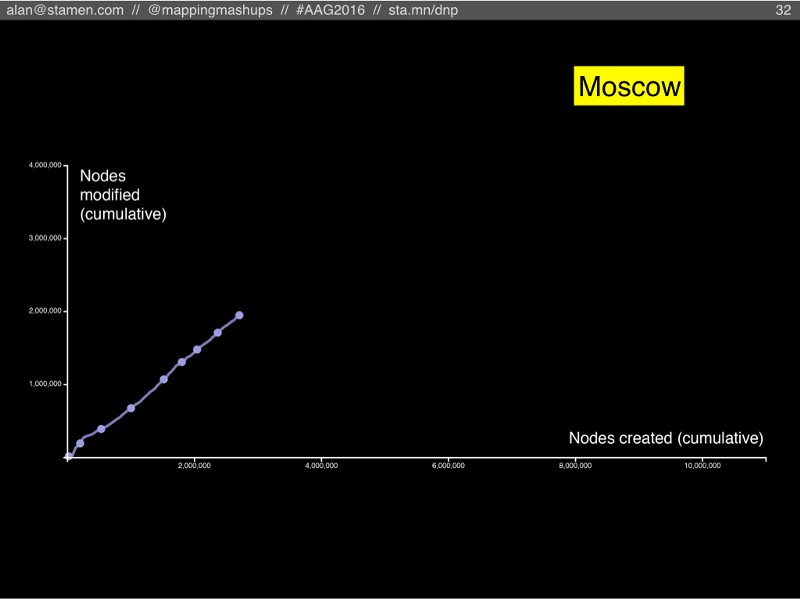
Finally, Moscow. Another well-mapped city with a strong community, similar to London or Berlin. But of all the cities we’ve looked at, the slope of the line is the steepest: Moscow has its own blend of node creators and node maintainers, with significantly higher rate of maintenance than anywhere else! Is this a cultural difference within the OSM community? Does it mean Moscow’s map is more up-to-date and better maintained? It will be fascinating to find out!
Finally, these charts can’t really tell us anything about how much maintenance is necessary to keep OSM at some minimum level of quality. But we can start thinking about what that equation would look like. We know there are at least two reasons why we need maintenance: to fix human error in the node creation process, and to keep OSM up-to-date to reflect changes out in the real world. The human error rate is a function of the number of new nodes (and also errors during the process of maintenance, we can ignore those for now), while the rate of real-world change is a function of the number of features in OSM that reflect features in the real world. If OSM decides to include features for blade of grass, that’s a lot of maintenance edits that will be required whenever someone mows the lawn.
Here’s what a first stab at that equation looks like. All the values are unknowns at this point, but one thing is clear: “map gardening” shouldn’t be and can’t be just an afterthought. In the long run, without maintenance OSM won’t add up to much.

I would love to hear what you think about this research. Please get in touch!
UPDATE: Bill Morris was quick to give an opinion: “I’m definitely voting ‘Borgesian map’ as the likely outcome here.” …which made me think, I should do a twitter poll. So let me know what you think will happen with OpenStreetMap. Remember that it might be years or decades before we know for sure:
